Boiler corrosion is a common issue that can lead to costly repairs and unsafe operations. Did you know that nearly 30% of boiler failures are due to corrosion-related problems? In this post, you will learn how to identify the causes of corrosion, detect early signs, and implement safe water treatment practices to protect your system. By following these essential guidelines, you can minimize risks associated with flue gas and carbon monoxide, ultimately ensuring reliable boiler performance and safety. If you've been struggling with boiler maintenance, this information will be invaluable in keeping your system running smoothly.
Identifying the Causes of Boiler corrosion
Understanding the causes of boiler corrosion is critical for effective prevention. Common corrosive agents, such as amine and water chemistry, have significant effects on HVAC Supplies surfaces. Additionally, the presence of oxygen and carbon dioxide can lead to issues like hydrogen embrittlement, exacerbating corrosion in recovery boilers. This section will explore these factors in detail, providing valuable insights to help you protect your boiler system.
Common Corrosive Agents in Boiler Systems
When it comes to boiler systems, understanding the impact of common corrosive agents like HVAC Parts is essential to preventing costly damage. One significant hazard is the presence of oxygen, which can lead to the formation of iron oxide on carbon steel surfaces. This oxide not only weakens the metal but also promotes further corrosion, reducing the lifespan of your boiler system. Keeping oxygen levels in check through proper water treatment can minimize this risk.
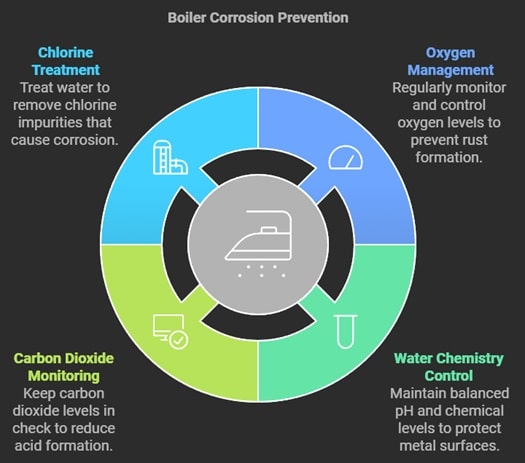
Another critical factor contributing to corrosion is the water chemistry used in your boiler. Improper pH levels can result in the deterioration of metal alloys, increasing susceptibility to leaks and Radiant Heating and Cooling failures. Regular monitoring of chemical balance is vital to ensure your boiler operates smoothly and efficiently, ultimately saving you money in repair and maintenance costs. Understanding how specific agents interact with your boiler components will empower you to take proactive HVAC Supplies measures.
Carbon dioxide is also a significant player in Boiler corrosion, especially in low-pH environments. It can react with water to form carbonic acid, leading to accelerated deterioration of both carbon steel and alloy components. Identifying and controlling these corrosive agents is crucial for your boiler's integrity and performance:
- Monitor oxygen levels to prevent iron oxide formation.
- Regularly check water chemistry to maintain proper pH levels.
- Be aware of carbon dioxide's effects on metal components.
Impact of Water Chemistry on Metal Surfaces
Water chemistry plays a pivotal role in the maintenance and operation of boiler systems. Fresh water must be appropriately treated to remove impurities that can lead to corrosion. For instance, elevated levels of chlorine concentration can interact negatively with metal surfaces, causing increased wastage over time and leading to potential failures in the system.
Maintaining the right pH levels in your boiler is essential to prevent carbon-related corrosion. If the water becomes too acidic, it can cause rapid deterioration of metal components, underscoring the importance of regular testing and adjustments. Incorporating chemicals that stabilize water chemistry can help mitigate these risks and extend the life of the boiler.
Experiencing waste from boiler systems can be costly, both in terms of repairs and operational efficiency. To avoid these issues, ensure that you monitor and adjust water chemistry consistently. Taking proactive actions like these will assure that your system remains functional and efficient while reducing the likelihood of corrosion-related failures:
- Regularly test water for chlorine and carbon levels.
- Implement treatments to maintain balanced pH levels.
- Monitor for signs of corrosion in metal surfaces to take corrective actions early.
Role of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Corrosion
Oxygen plays a critical role in the corrosion of boiler systems, especially in the presence of water vapor. When oxygen interacts with moisture, it can lead to the formation of hydroxides that contribute to rust on metal surfaces. Regular inspection of equipment, such as piping and fittings, enables you to identify and address any corrosion risks early, preventing costly repairs.
Carbon dioxide also significantly impacts Boiler corrosion by reacting with water to form carbonic acid, particularly in cooling tower systems where water quality may fluctuate. This acid can cause rapid deterioration of metal components, making it essential to monitor carbon dioxide levels closely. By implementing effective water treatment protocols, you can reduce carbonic acid formation and protect your boiler's integrity.
In wastewater treatment settings, both oxygen and carbon dioxide must be carefully managed to minimize corrosion risks. Keeping an eye on water chemistry during operations not only helps in corrosion prevention but also enhances the overall efficiency of your system. Understanding how these gases affect your boiler components allows you to take proactive measures and ensure its optimal performance over time.
Detecting Early Signs of Corrosion for Safe Operation
Recognizing the early signs of corrosion in your boiler is vital for maintaining safety and efficiency. You'll learn to identify visual indicators of corrosion damage, explore performance issues linked to fouling, and understand diagnostic tests essential for accurate detection. Monitoring water quality in your boiler system is crucial, particularly during wastewater treatment processes, to prevent problems like improper boiler blowdown.
Visual Indicators of Corrosion Damage
Visual indicators of corrosion damage in your boiler can often be subtle but critical to identify early. One of the most prominent signs is the formation of iron oxide, commonly known as rust, on visible metal surfaces. As you inspect your boiler, look for any discoloration, flaking, or rough patches that could signal the presence of rust and potentially higher operational pressures that affect performance.
Additionally, pay attention to any unusual changes in your water heating system. If you're using distilled water and notice an increase in sediment or unusual particles in the water, it may signal underlying corrosion issues. Consistently monitor any changes in temperature or pressure readings; fluctuations can indicate inefficient heat transfer due to corrosion-related blockages.
Using sensors to monitor temperature, pressure, and water quality provides valuable insights into the health of your boiler system. These sensors can alert you to any abnormal conditions that could precede significant damage. Regularly reviewing the data from these sensors will help you maintain optimal operation and address corrosion early on.
- Look for signs of iron oxide and rust on metal surfaces.
- Monitor changes in water quality and heating efficiency.
- Utilize sensors for real-time data on temperature and pressure.
Performance Issues Linked to Corrosion
Corrosion in your boiler system can lead to significant performance issues, particularly regarding the alkalinity of the water supply. When alkalinity levels drop, it can result in increased acidity, which deteriorates metal components like stainless steel. This deterioration can cause leaks and inefficiencies, ultimately impacting your operation’s effectiveness and safety.
Another critical aspect to monitor is the accumulation of hydrogen sulfide in the water supply, which can exacerbate corrosion. If left unchecked, hydrogen sulfide can create weak points in the boiler materials, leading to premature failure. Regular testing for these corrosive substances, combined with appropriate scavenger treatments, can help you maintain system integrity and performance.
Additionally, assessing the overall conditions of your boiler system can reveal performance issues stemming from corrosion. Unusual fluctuations in pressure or temperature can indicate blockages caused by corrosion-related debris. By conducting frequent inspections and maintaining a proactive approach to your water treatment, you can address these challenges before they escalate into costly repairs.
Diagnostic Tests for Accurate Detection
Conducting diagnostic tests is essential for accurately detecting corrosion in your boiler system. Regular testing can identify chemical reactions that contribute to rust and degradation, particularly in cast iron pressure vessels. By evaluating the integrity of your boiler, you can address potential issues before they escalate.
One effective method involves using non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, such as ultrasonic testing, to assess wall thickness and detect early signs of corrosion. This approach allows you to inspect the tank without causing damage, providing valuable insights into the boiler's structural health. Monitoring any changes over time can signify the onset of corrosion, giving you the ability to intervene promptly.
Additionally, employing corrosion monitoring probes can help track the corrosion rate within your boiler system. These devices measure the effect of natural gas and other factors on the metal surfaces, alerting you to potential risks. By integrating these technologies into your maintenance routine, you can ensure your boiler operates safely and efficiently:
- Conduct regular diagnostic tests to detect early signs of corrosion.
- Utilize non-destructive testing methods for accurate assessments.
- Install corrosion monitoring probes to track changes over time.
Implementing Safe Water Treatment Practices
Implementing safe water treatment practices is essential for preventing corrosion in boiler systems. You will learn about the importance of water softening and deaeration in reducing mineral hardness that can lead to corrosion. Controlling pH levels is critical to maintaining the integrity of steel components. Additionally, effective use of chemical treatments, such as nitrite and sulfur dioxide, can significantly enhance boiler performance by combating corrosive agents.
Importance of Water Softening and Deaeration
Water softening is a vital process in preventing Boiler corrosion. By removing hard minerals like calcium and magnesium, you can reduce the risk of scale formation that can hinder heat transfer. When scale coats surfaces in your boiler, it can create hot spots that contribute to localized overheating, ultimately damaging the metal structure and advancing corrosion.
Deaeration plays an equally important role in maintaining a corrosion-free atmosphere within your boiler system. By eliminating dissolved gases, particularly oxygen, you minimize the conditions under which corrosion can occur. The presence of oxygen cathodes can accelerate the oxidation process, so utilizing a deaerator ensures you maintain a protective environment for your metal components, leading to increased longevity.
Incorporating polymer-based treatments can also provide additional protection against corrosion. These innovative solutions coat the metal surfaces, creating a barrier that resists corrosive agents like water and oxygen. By selecting the right polymer treatments for your boiler, you can enhance overall performance while safeguarding copper and other metal components from premature wear and deterioration.
Controlling pH Levels to Prevent Corrosion
Controlling pH levels in your boiler system is essential to prevent corrosion of metal components. A balanced pH level, generally between 8.5 and 9.5, helps create a protective environment for your metal surfaces, mitigating the risk of acidic corrosion. For effective management, conducting regular water testing will help you ensure that your boiler's water chemistry remains within the ideal range, thus extending the lifespan of your boiler system.
Using sodium sulfite as an oxygen scavenger can significantly assist in maintaining desired pH levels while also curbing corrosion risk. This chemical not only reduces the presence of oxygen but can also help stabilize pH levels, leading to improved performance of metal surfaces within the boiler. Implementing such chemical treatments is crucial to safeguarding metal integrity and enhancing operational efficiency.
To adopt these practices effectively, it's important to monitor your boiler water continuously. Inconsistent pH levels can contribute to significant corrosion issues, making treatment essential. Incorporate a routine that includes testing for pH levels, assessing for sulfite presence, and making necessary adjustments to maintain optimal conditions:
- Regularly test water for pH levels.
- Utilize sodium sulfite to control oxygen and stabilize pH.
- Monitor for signs of corrosion and adjust treatments as needed.
Using Chemical Treatments Effectively
Using chemical treatments effectively is crucial for preventing Boiler corrosion. For instance, incorporating sulfur compounds into your water treatment regimen can help neutralize acids that form during combustion processes. This reduces the risk of acid corrosion, which can damage metal components, particularly in areas like the economizer where temperatures and pressures fluctuate significantly.
Maintaining proper alkali levels in the boiler water is another essential practice. Alkali agents work to stabilize pH levels, protecting metal surfaces from corrosion. By regularly monitoring and adjusting these chemical treatments, you can ensure that your system operates within a safe range and minimize the chance of leaks and other failures that could disrupt your operations.
Lastly, pay attention to the functionality of valves within your boiler system. Corrosion can start in places where water flow is restricted or where chemical treatments are not evenly distributed. Ensuring that valves are maintained and inspected regularly allows for optimal chemical flow, enhancing the effectiveness of your treatments and extending the life of your boiler components.
Applying Protective Measures Against Corrosion
Selecting corrosion-resistant materials is essential for your boiler system's longevity and effectiveness. You'll explore utilizing protective coatings and linings that enhance passivation and prevent sludge buildup. Additionally, installing sacrificial anodes can significantly reduce corrosion risk. These measures work together to maintain optimal performance and safeguard your boiler from harmful agents like sodium hydroxide and moisture that can lower the dew point.
Selecting Corrosion-Resistant Materials
Selecting corrosion-resistant materials for your boiler system is a key strategy in preventing damage and ensuring efficient operation. Materials such as stainless steel or alloyed steels provide enhanced protection against corrosive agents like sulfide and can significantly extend the lifespan of your components. When these materials are combined with a well-maintained boiler feedwater system, they become even more effective at resisting the impacts of corrosion.
Understanding the role of magnetite is essential when working with ferrous materials in boiler systems. Magnetite can form as a protective barrier on metal surfaces, providing additional defense against corrosive elements. By ensuring appropriate production of magnetite through controlled water chemistry and temperature, you can help shield your boiler's components and maintain their integrity over time.
Additionally, keep in mind that the selection of materials should also consider operational factors, such as flue gas temperatures and pressure variations. By opting for materials specifically designed to withstand high-temperature environments, you can further minimize the risk of corrosion, leading to more reliable performance overall. Being proactive in material selection can make a significant difference in reducing maintenance costs and enhancing the efficiency of your boiler system.
Utilizing Protective Coatings and Linings
Utilizing protective coatings and linings is a key step in preventing Boiler corrosion and ensuring your system operates safely. These coatings serve as a barrier between the metal surfaces and the corrosive agents in the environment, such as moisture and oxygen. When selecting a coating, look for products that also act as oxygen scavengers, significantly minimizing the corrosion risk on components like pumps.
Another practical solution is to employ desiccants in conjunction with protective linings. Desiccants absorb moisture from the air, further preventing conditions that lead to corrosion. Combining these strategies enhances the overall productivity of your boiler system by reducing maintenance needs and improving operational efficiency over time.
Additionally, consider installing sacrificial anodes within your boiler system. These anodes corrode in place of your critical metal components, providing a cost-effective solution to combat corrosion. By implementing these protective measures effectively, you can substantially increase the longevity and reliability of your boiler system:
- Choose protective coatings that resist corrosive agents.
- Incorporate desiccants to reduce moisture exposure.
- Install sacrificial anodes to protect vital components.
Installing Sacrificial Anodes in the System
Installing sacrificial anodes in your boiler system is a proactive measure that can significantly reduce the risk of corrosion. These anodes, often made of materials like magnesium or zinc, corrode before the essential metal components of your system do. By sacrificing themselves, they absorb the corrosive energies present in the liquid environment, thereby protecting your boiler from damage and extending its lifespan.
During the installation process, careful consideration of placement is vital. Anodes should be strategically positioned to ensure optimal diffusion of protection against corrosive agents. For instance, installing them in areas where sodium sulfite concentrations are high can enhance their efficacy in combating corrosion caused by oxygen and moisture stress, which are prevalent in boiler systems.
Regular monitoring of sacrificial anodes is essential to determine when they need replacement. Neglecting this aspect can lead to increased vulnerability to corrosion, resulting in costly repairs. To maintain a robust preventative strategy against Boiler corrosion, ensure you periodically check the condition of these anodes and replace them as needed:
- Assess the condition of anodes regularly.
- Replace anodes when they show significant wear.
- Ensure anodes are installed in high-risk corrosion areas.
Operating Boilers Safely to Minimize Corrosion
Managing pressure and temperature parameters is crucial to prevent Boiler corrosion and enhance efficiency. Proper startup and shutdown procedures help minimize acid and chloride interactions, while regular maintenance and cleaning routines can significantly reduce erosion risks. This section will guide you through best practices to ensure your boiler operates safely and effectively, safeguarding it from harmful corrosive agents.
Managing Pressure and Temperature Parameters
Managing pressure and temperature parameters is essential for preventing Boiler corrosion and ensuring efficient operation. By closely monitoring these variables, you can minimize the risk of issues such as crevice corrosion, which can develop in hidden gaps where water and contaminants can accumulate. Utilizing effective control systems will help you maintain optimal conditions, protecting your investment while ensuring reliable performance.
Additionally, implementing regular checks of relief valves can prevent excessive pressure buildups that could lead to catastrophic failures. Understanding the correlation between pressure levels and various corrosive agents, such as chlorine dioxide, is crucial. By maintaining a balanced system, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of contamination that jeopardizes the integrity of your boiler components.
Regularly scheduled maintenance sessions can help you avoid downtime while ensuring safety. Establishing a routine for checking pressure and temperature settings sets the foundation for consistent operations, allowing you to identify and rectify issues before they escalate. By prioritizing these practices, you take proactive measures to keep your boiler system functioning smoothly:
- Monitor pressure and temperature levels continuously.
- Inspect relief valves regularly to avoid pressure overloads.
- Maintain a routine maintenance schedule to reduce downtime.
Proper Startup and Shutdown Procedures
Proper startup and shutdown procedures are essential for preventing Boiler corrosion and ensuring the longevity of your system. During startup, it’s important to allow the feedwater heater to function correctly by ensuring that the water entering the boiler is free from oxygen, which is a common contributor to pitting corrosion. By maintaining controlled conditions right from the beginning, you set a solid foundation for effective boiler operation and minimize risks associated with fatigue and other forms of wear.
When shutting down a boiler, implementing an effective layup process is crucial for protecting metal components from corrosion. This process involves draining the system and ensuring that it is properly cleaned and dried before a prolonged shutdown. Utilizing appropriate corrosion inhibitors during this phase can help prevent the formation of rust and other harmful deposits that may develop during idle periods.
In addition, monitoring residual moisture levels during both startup and shutdown can mitigate the risks of corrosion. After a layup, it’s essential to ensure that the boiler is kept in a dry environment to avoid creating conditions that encourage corrosive attack. By focusing on these procedures and solutions, you help maintain the integrity of your boiler system for years to come.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning Routines

Conducting regular maintenance and cleaning routines is vital for preserving the integrity of your boiler system and preventing corrosion. By routinely inspecting key components and removing any buildup of iron or sediment, you can significantly minimize risks associated with corrosion. Implementing a structured maintenance schedule ensures you address potential issues before they escalate, ultimately saving you time and repair costs.
In addition to physical inspections, monitoring the quality of the fluid used in your system is crucial. Pay particular attention to the presence of electrolytes, which can contribute to corrosive reactions when combined with contaminants like oil or nitrogen. Regularly testing fluid quality and maintaining appropriate chemical levels will help you identify any deviations that could lead to accelerated degradation of your boiler components.
To effectively enhance the longevity of your system, consider adopting a comprehensive cleaning approach that includes both chemical treatments and physical cleaning methods. Utilizing suitable cleaning agents can effectively dissolve deposits that may harbor corrosive agents, while also ensuring that all surfaces are free from oil and debris. By integrating these practices into your routine, you enhance your boiler’s performance and protect it from damaging corrosion:
- Inspect and clean components to remove iron or sediment buildup.
- Monitor fluid quality for electrolytes and chemical balance.
- Adopt both chemical and physical cleaning methods to ensure system integrity.
Developing a Comprehensive Corrosion Prevention Plan
To develop a comprehensive corrosion prevention plan for your boiler system, you must prioritize scheduling routine inspections and assessments. These checks identify issues like water hammer and potential failures in your boiler feedwater pump before they escalate. Additionally, training personnel on prevention techniques and keeping detailed records for compliance will ensure that your operations remain efficient and safe, ultimately protecting vital components like your superheater from deterioration.
By integrating these practices, you can enhance troubleshooting efforts and maintain the integrity of your system, safeguarding against corrosion caused by factors like organic matter buildup.
Scheduling Routine Inspections and Assessments
Scheduling routine inspections and assessments is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your boiler water system. Regular checks allow you to identify issues such as electrolysis, which can lead to serious corrosion problems if left unaddressed. By adhering to a consistent inspection schedule, you can catch early signs of trouble, such as metal decomposition or unexpected fluctuations in water quality.
During these inspections, you should assess the entire system, paying close attention to areas where ion exchange occurs, like water softeners. Ensuring that these systems are functioning correctly helps to maintain balanced water conditions that prevent corrosion. For example, without proper maintenance, ion exchange resin can degrade, allowing harmful components to infiltrate your boiler water system.
Incorporating plastic components where feasible can also help reduce corrosion risks. Unlike metal, plastic components are less susceptible to rust and other corrosive wear, making them a valuable alternative in certain applications. By regularly examining both your metal and plastic parts, you ensure that all components work together efficiently, contributing to the overall longevity of your boiler system.
Training Personnel on Prevention Techniques
Training personnel on corrosion prevention techniques is crucial for the effective management of boiler systems. By ensuring that your team understands the role of corrosion inhibitors, they can effectively apply these chemicals to mitigate risks associated with hydrogen sulfide and sulfate. This knowledge empowers them to identify problem areas, such as the accumulation of contaminants in pipes, that may lower efficiency and heat transfer.
Hands-on training sessions can provide your staff with practical insights into monitoring water quality, which is essential in detecting early signs of corrosion. By familiarizing them with the signs of corrosion such as pitting or rust formation on key components, they become better equipped to react swiftly. Encouraging consistent testing and monitoring of variables like pH levels will help in maintaining a balanced system conducive to prolonging the life of your boiler.
Incorporating real-world scenarios during training can enhance understanding and ensure knowledge retention. For example, by showcasing the impact of neglecting regular inspections or failing to use corrosion inhibitors effectively, you can illustrate the potential consequences of poor maintenance practices. This approach reinforces the importance of proactive measures, ultimately contributing to the reliability and safety of your boiler operations.
Keeping Detailed Records for Compliance
Keeping detailed records for compliance in your boiler system is crucial for effective water purification and preventing corrosion. By meticulously documenting your maintenance activities, chemical treatments, and water quality tests, you create a solid trail of accountability. These records not only help you track the history of your heat exchanger’s performance but also facilitate compliance with regulatory standards that pertain to boiler operations.
Your records should also include periodic assessments of materials for porosity and corrosion, enabling you to identify trends over time. For instance, tracking carbon dioxide levels can highlight potential risks before they become critical. By maintaining detailed logs, you can pinpoint issues and adjust your corrosion prevention strategies promptly, ultimately safeguarding your boiler system against damage.
Regular reviews of your compliance records can reveal opportunities for improving operational efficiency and enhancing safety protocols. By analyzing historical data, you can gain insights into the effectiveness of your water purification methods and make informed decisions moving forward. This proactive approach not only addresses immediate concerns but also contributes to the long-term reliability of your boiler and its components.
Conclusion
Preventing Boiler corrosion is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of your system. By understanding the causes of corrosion and implementing safe water treatment practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of costly damage. Regular inspections, proper chemical treatments, and employee training enhance your capability to spot issues early and take corrective actions. Ultimately, prioritizing these essential guidelines protects your investment and ensures the reliable operation of your boiler.
Resources:
Learn about HVAC
Learn about boilers